In nearly every single instance of product development, no matter what industry it’s for, prototyping is a necessary stage that will ultimately determine whether your production efforts will be successful or not. The rise of rapid prototyping has made it both easy and affordable to quickly iterate a plastic prototype. However, there are a range of manufacturing technologies that are capable of producing a plastic prototype, and knowing which one you should use will optimize the entire product development process.
Let’s take a look at how to create a plastic prototype with 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding and vacuum casting. While each provides its own benefits, knowing the inner workings of the technology, compatible materials and common applications will help you decide which rapid manufacturing technique is best suited for your plastic prototype.
How to Create a Plastic Prototype With 3D Printing
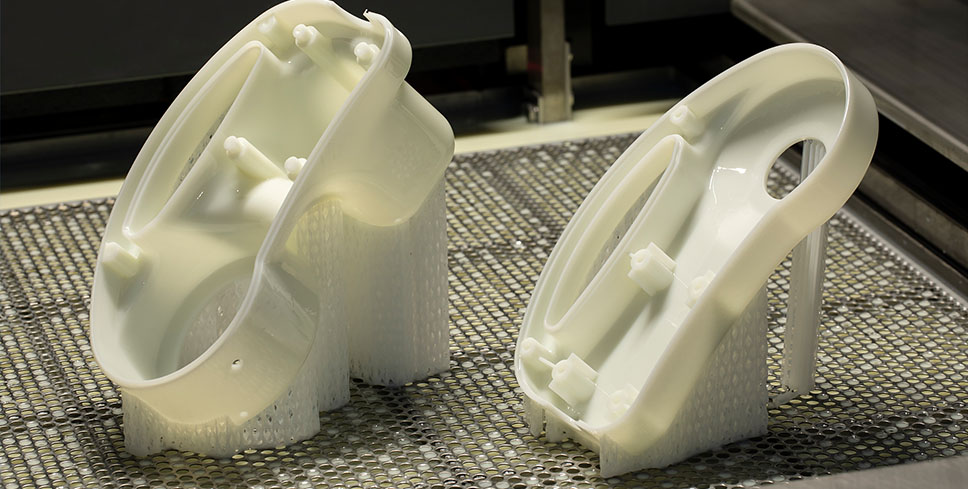
Additive manufacturing–more commonly known as 3D printing— is actually a blanket term that encompasses a handful of different manufacturing technologies. The three most popular options for producing plastic prototypes is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
FDM 3D printing uses an extrusion process to deposit plastic material in a layer-by-layer fashion until an object is created. This is the most widely used form of 3D printing, and almost exclusively employed by the maker community and consumers. Industrial-grade FDM 3D printers can be used to manufacture plastic prototypes in high resolution and strength, depending on the material used.
If you want to create a colorful prototype that will not serve much of a mechanical purpose, PLA (Polylactic Acid) is an exceptionally diverse and affordable material. It can even be fused with wood and metal composites to conjure up exoctic filaments, and also spliced with mechanically superior materials like carbon fiber to enhance functionality.
But on the industrial stage, most other 3D printing materials tend to offer more functionality than PLA. For instance, ABS is an ancient material used to create plastic prototypes, and is ideal for functional prototypes that will undergo a fair amount of impact, wear or high temperatures. This material is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries, and is also well-suited for electronics, consumer goods and more.
Nylon is a material that can be used with both FDM and SLS 3D printing, and is known to be tough and flexible. It’s perfect for functional prototypes, as well as gears and tooling. When you need a plastic prototype that has rubber-like flexibility, TPE and TPU are great 3D printing materials to utilize. The rubber-like characteristics of this material are beneficial when producing plastic prototypes for protective gear, phone cases, and various industrial components.
Other FDM materials include PETG, a thermoplastic that is most commonly used to create water bottles; and Polycarbonate (PC), which is an industrial-grade material that is used to produce plastic prototypes that will be used for engineering applications and face harsh environments.
Instead of using filament, SLA 3D printing utilize plastic resin materials to create plastic prototypes. The process features a high-powered laser that solidifies the model from a vat of resin. This process is widely used for various prototyping purposes, especially within the medical, dental, and consumer goods space.
Meanwhile, with SLS technology, the most commonly used material is Nylon (PA 11 or PA 12). Since this technique uses a high-powered laser to sinter powder together into a 3D model, both the material and print quality is superior to FDM. Plastic prototypes created via SLS 3D printing are generally more functional, have a higher resolution, and can be more flexible and durable than FDM prints.
When should you use 3D printing to create a plastic prototype?
Well, the best time to use 3D printing for your prototyping needs is when you have a small volume that you need produced as quickly as possible. Additive manufacturing helps designers and engineers to cut down on product development time, as they can rapidly iterate their plastic prototype and test or modify the design. However, if you need to produce a large batch of plastic prototypes, or require superior mechanical properties to what 3D printing can offer, there’s likely a more preferable rapid manufacturing technique for you.
How to Create a Plastic Prototype With CNC Machining
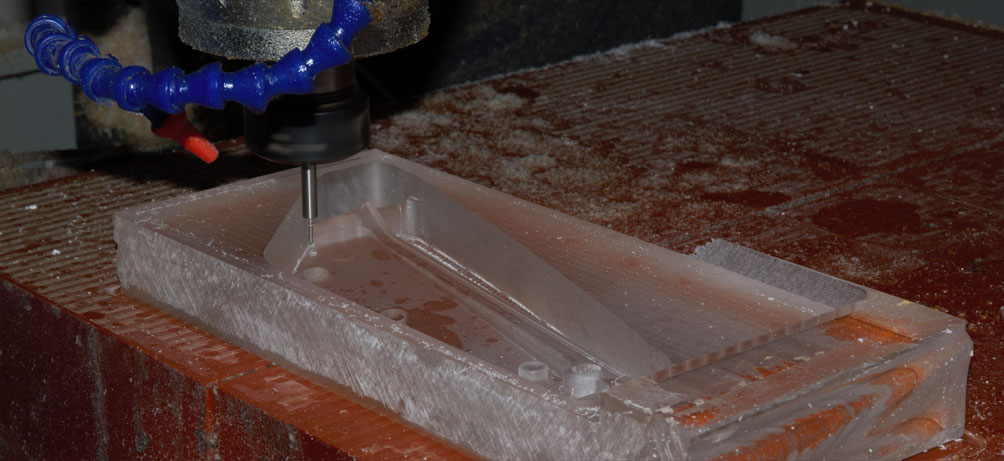
Another fast-paced and viable option for creating functional plastic prototypes is with CNC milling. This technology uses a variety of different sized tools to carve out a 3D model from a solid block of material. Compared to 3D printing, CNC machining offers more potential for threads and undercuts, tight tolerances, reduced size limitations and more surface finishes. Depending on the complexity of the plastic prototype model and the manufacturing service used, CNC milling can also provide extremely quick turnaround times. Learn more about plastic machining prototypes.
While producing injection molding tooling for a small volume of plastic prototypes is generally too expensive, CNC machining allows you to test the form, fit and function of injection molded parts without having to produce injection mold tooling. There are a wide range of plastics that 3ERP offers through our CNC machining service, including ABS, PC, PP, POM, PMMA (Acrylic), HDPE, Teflon, PEEK and many others. To find out which type of material is ideal for your plastic prototype, you can contact our team of experts for more information.
When should you use CNC machining to create a plastic prototype?
There are a handful of advantages that CNC machining holds over 3D printing technology, one of which is the mechanical quality and available range of thermoplastic materials. Parts that are CNC machined also bestow improved structural integrity upon plastic parts, which is essential when creating functional prototypes. Typically, this production method is used to create plastic prototypes that will be tested under the same conditions as injection molded parts.
How to Create a Plastic Prototype With Injection Molding
Although injection molding and rapid tooling is sometimes used for mass production, it also offers a fast and affordable way to produce plastic prototypes. After creating a metal die, plastic resin is sent into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected with force into a metal die. This plastic is rapidly cooled into a solid part, making a plastic prototype that has a high quality surface finish and better mechanical properties than 3D printing, for example.
Some of the most popular plastics used for injection molding are also utilized in 3D printing and CNC machining. These include ABS, PC, Nylon, HIPS, PP, as well as Polyethylene.
Just as we described with 3D printing, ABS material is great for plastic prototypes that require impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance. Injection molded PC is completely unique from most other thermoplastics, as it is able to undergo deformation without cracking or breaking, and is best suited for products like eyewear lenses, medical devices and automotive components.
With injection molding, Nylon is used to produce plastic prototypes that promote stability and resistance to environmental factors like abrasion and chemicals. On the flip side, polyethylene, which comes in the form of HDPE or LDPE, offers a wide range of distinct mechanical properties, including high levels of ductility, tensile strength and resistance to impact and moisture absorption.
To learn more about the plastic materials that 3ERP offers for injection molding, contact our team of experts!
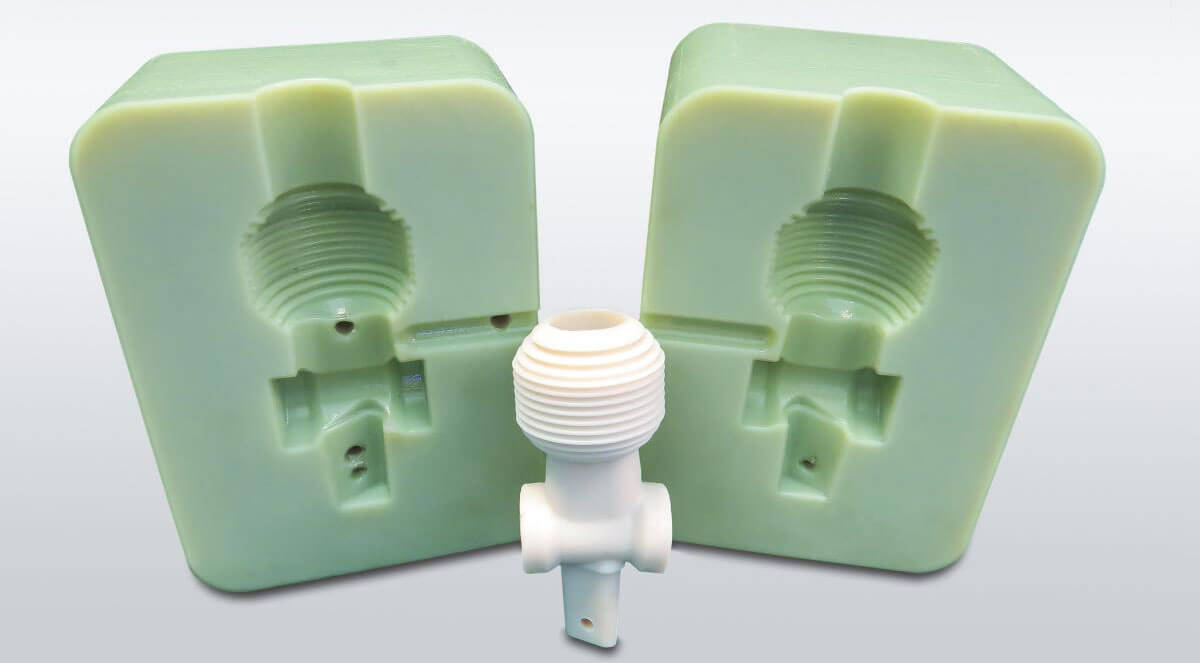
When should you use injection molding to create a plastic prototype?
Injection molding remains the most popular method for full-scale production and prototyping, and is widely used across many industries, including consumer electronics, home appliances, medical devices, automotive and aerospace.
How to Create a Plastic Prototype With Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is another manufacturing tool that can be utilized to produce plastic prototypes. This distinct technique is performed in a three-step process, starting with the production of your CAD design into a master model, which can be done with 3D printing or CNC machining. Once the master mold is complete, silicone-based casting molds are developed and filled with casting resins into the cavity of the mold. As for materials, vacuum casting is compatible with an array of materials that range from opaque to transparent, as well as many colors.
Each mold can produce around 25 prototypes, and the turnaround time is an average of two weeks. All in all, it’s a quick way to actualize your design into a plastic prototype, pushing the development process closer to mass production.
When should you use vacuum casting to create a plastic prototype?
For plastic prototype production, vacuum casting is generally used for small production runs, especially for objects such as casings or housings. This technique is also utilized for visual models or prototypes that don’t serve much of a mechanical purpose. At 3ERP, we offer a wide range of plastic materials for vacuum casting.
Conclusion
All in all, finding the right manufacturing technology and material is critically important to the success of your plastic prototype. Our team at 3ERP is more than happy to help you find the right process for you, so contact us today to learn more about our rapid manufacturing services.










